

|
NS-3 based Named Data Networking (NDN) simulator
ndnSIM: NDN, CCN, CCNx, content centric networks
|
Overall ndnSIM documentation |


|
NS-3 based Named Data Networking (NDN) simulator
ndnSIM: NDN, CCN, CCNx, content centric networks
|
Overall ndnSIM documentation |
To obtain simulation results, you would need to connect to one or more trace sources provided by ndnSIM classes.
It is also possible to use existing trace helpers, which collects and aggregates requested statistical information in text files.
Tracing the aggregate number of Interests/Data packets forwarded by an NDN node
The following example enables tracing on all simulation nodes:
// the following should be put just before calling Simulator::Run in the scenario ndn::L3AggregateTracer::InstallAll ("aggregate-trace.txt", Seconds (1.0)); Simulator::Run (); ...Output file format is tab-separated values, with first row specifying names of the columns. Refer to the following table for the description of the columns:
Column Description Time simulation time Node node id, globally unique FaceId interface ID (-1 for combined metric) Type Type of measurements:
- InInterests measurements of incoming Interests
- OutInterests measurements of outgoing Interests
- DropInterests measurements of dropped Interests
- InData measurements of incoming Data
- OutData measurements of outgoing Data
- DropData measurements of dropped Data
- InNacks measurements of incoming NACKs
- OutNacks measurements of outgoing NACKs
- DropNacks measurements of dropped NACKs
- SatisfiedInterests measurements of satisfied Interests
- TimedOutInterests measurements of timed out Interests
Packets absolute number of packets within last averaging period (number of packets). Kilobytes absolute number of kilobytes transferred within the last averaging period (number of packets).
Tracing the rate in bytes and in number of packets of Interest/Data packets forwarded by an NDN node
The following example enables tracing on all simulation nodes:
// the following should be put just before calling Simulator::Run in the scenario ndn::L3RateTracer::InstallAll ("rate-trace.txt", Seconds (1.0)); Simulator::Run (); ...Output file format is tab-separated values, with first row specifying names of the columns. Refer to the following table for the description of the columns:
Column Description Time simulation time Node node id, globally unique FaceId interface ID (-1 for combined metric) Type Type of measurements:
- InInterests measurements of incoming Interests
- OutInterests measurements of outgoing Interests
- DropInterests measurements of dropped Interests
- InData measurements of incoming Data
- OutData measurements of outgoing Data
- DropData measurements of dropped Data
- InNacks measurements of incoming NACKs
- OutNacks measurements of outgoing NACKs
- DropNacks measurements of dropped NACKs
- InSatisfiedInterests measurements of incoming satisfied Interests
- InTimedOutInterests measurements of incoming timed out Interests
- OutSatisfiedInterests measurements of outgoing satisfied Interests
- OutTimedOutInterests measurements of outgoing satisfied Interests
Packets estimated rate (EWMA average) of packets within the last averaging period (number of packets/s). Kilobytes estimated rate (EWMA average) within last averaging period (kilobytes/s) PacketsRaw absolute number of packets within last averaging period (number of packets). KilobytesRaw absolute number of kilobytes transferred within the last averaging period (number of packets).
This tracer is similar in spirit to ndn::L3RateTracer, but it currently traces only packet drop on layer 2 (e.g., due to transmission queue overflow).
The following example enables tracing on all simulation nodes:
// the following should be put just before calling Simulator::Run in the scenario L2RateTracer::InstallAll ("drop-trace.txt", Seconds (0.5)); Simulator::Run (); ...Output file format is tab-separated values, with first row specifying names of the columns. Refer to the following table for the description of the columns:
Column Description Time simulation time Node node id, globally unique Interface interface name (currently only “combined”) Type Type of measurements:
- Drop measurements of dropped packets
Packets estimated rate (EWMA average) of packets within the last averaging period (number of packets/s). Kilobytes estimated rate (EWMA average) within last averaging period (kilobytes/s) PacketsRaw absolute number of packets within last averaging period (number of packets). KilobytesRaw absolute number of kilobytes transferred within the last averaging period (number of packets).
Note
A number of other tracers are available in plugins/tracers-broken folder, but they do not yet work with the current code. Eventually, we will port most of them to the current code, but it is not our main priority at the moment and would really appreciate help with writing new tracers and porting the old ones.
This example (ndn-tree-tracers.cc) demonstrates basic usage of Packet-level trace helpers.
In this scenario we will use a tree-like topology, where consumers are installed on leaf nodes and producer is in the root of the tree:
The corresponding topology file (topo-tree.txt):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | # topo-tree.txt
router
#node city y x mpi-partition
leaf-1 NA 80 40 1
leaf-2 NA 80 20 3
leaf-3 NA 80 0 2
leaf-4 NA 80 -20 4
rtr-1 NA 60 20 1
rtr-2 NA 60 0 2
root NA 40 10 0
link
# from to capacity metric delay queue
leaf-1 rtr-1 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
leaf-2 rtr-1 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
leaf-3 rtr-2 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
leaf-4 rtr-2 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
rtr-1 root 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
rtr-2 root 10Mbps 1 1ms 100
|
Example simulation (ndn-tree-tracers.cc) scenario that utilizes trace helpers:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | // ndn-tree-tracers.cc
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/ndnSIM-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
AnnotatedTopologyReader topologyReader ("", 1);
topologyReader.SetFileName ("src/ndnSIM/examples/topologies/topo-tree.txt");
topologyReader.Read ();
// Install CCNx stack on all nodes
ndn::StackHelper ccnxHelper;
ccnxHelper.SetForwardingStrategy ("ns3::ndn::fw::BestRoute");
ccnxHelper.InstallAll ();
// Installing global routing interface on all nodes
ndn::GlobalRoutingHelper ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper;
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.InstallAll ();
// Getting containers for the consumer/producer
Ptr<Node> consumers[4] = { Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-1"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-2"),
Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-3"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-4") };
Ptr<Node> producer = Names::Find<Node> ("root");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
ndn::AppHelper consumerHelper ("ns3::ndn::ConsumerCbr");
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Frequency", StringValue ("100")); // 100 interests a second
// Each consumer will express unique interests /root/<leaf-name>/<seq-no>
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root/" + Names::FindName (consumers[i]));
consumerHelper.Install (consumers[i]);
}
ndn::AppHelper producerHelper ("ns3::ndn::Producer");
producerHelper.SetAttribute ("PayloadSize", StringValue("1024"));
// Register /root prefix with global routing controller and
// install producer that will satisfy Interests in /root namespace
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/root", producer);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root");
producerHelper.Install (producer);
// Calculate and install FIBs
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.CalculateRoutes ();
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (20.0));
ndn::L3AggregateTracer::InstallAll ("aggregate-trace.txt", Seconds (0.5));
ndn::L3RateTracer::InstallAll ("rate-trace.txt", Seconds (0.5));
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
|
To run this scenario, use the following command:
./waf --run=ndn-tree-tracers
The successful run will create rate-trace.txt and aggregate-trace.txt files in the current directly, which can be analyzed manually or used as input to some graph/stats packages.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 | # Copyright (c) 2012 Alexander Afanasyev <alexander.afanasyev@ucla.edu>
# install.packages ('ggplot2')
library (ggplot2)
# install.packages ('scales')
library (scales)
# install.packages ('doBy')
library (doBy)
#########################
# Rate trace processing #
#########################
data = read.table ("rate-trace.txt", header=T)
data$Node = factor (data$Node)
data$FaceId <- factor(data$FaceId)
data$Kilobits <- data$Kilobytes * 8
data$Type = factor (data$Type)
# exlude irrelevant types
data = subset (data, Type %in% c("InInterests", "OutInterests", "InData", "OutData"))
# combine stats from all faces
data.combined = summaryBy (. ~ Time + Node + Type, data=data, FUN=sum)
data.root = subset (data.combined, Node == "root")
data.leaves = subset (data.combined, Node %in% c("leaf-1", "leaf-2", "leaf-3", "leaf-4"))
# graph rates on all nodes in Kilobits
g.all <- ggplot (data.combined) +
geom_point (aes (x=Time, y=Kilobits.sum, color=Type), size=1) +
ylab ("Rate [Kbits/s]") +
facet_wrap (~ Node)
print (g.all)
# graph rates on the root nodes in Packets
g.root <- ggplot (data.root) +
geom_point (aes (x=Time, y=Kilobits.sum, color=Type), size=2) +
geom_line (aes (x=Time, y=Kilobits.sum, color=Type), size=0.5) +
ylab ("Rate [Kbits/s]")
print (g.root)
png ("root-rates.png", width=500, height=250)
print (g.root)
dev.off ()
###############################
# Aggreagate trace processing #
###############################
data = read.table ("aggregate-trace.txt", header=T)
data$Node = factor (data$Node)
data$FaceId <- factor(data$FaceId)
data$Type = factor (data$Type)
# exlude irrelevant types
data = subset (data, Type %in% c("InInterests", "OutInterests", "InData", "OutData"))
# Aggregate packet stats in 5-second intervals
data$Time5Sec = 5 * ceiling (data$Time / 5)
data.combined = summaryBy (. ~ Time5Sec + Node + Type, data=data, FUN=sum)
data.root = subset (data.combined, Node == "root")
data.leaves = subset (data.combined, Node %in% c("leaf-1", "leaf-2", "leaf-3", "leaf-4"))
# graph rates on all nodes in Packets
g.all <- ggplot (data.combined) +
geom_point (aes (x=Time5Sec, y=Packets.sum, color=Type), size=2) +
geom_line (aes (x=Time5Sec, y=Packets.sum, color=Type), size=0.5) +
ylab ("Number of transitted packets in 5 secon intervals") +
facet_wrap (~ Node)
print (g.all)
# graph rates on the root nodes in Packets
g.root <- ggplot (data.root) +
geom_point (aes (x=Time5Sec, y=Packets.sum, color=Type), size=2) +
geom_line (aes (x=Time5Sec, y=Packets.sum, color=Type), size=0.5) +
ylab ("Number of transitted packets in 5 secon intervals") +
ylim (c(0,2000))
print (g.root)
png ("root-5sec-counts.png", width=500, height=250)
print (g.root)
dev.off ()
|
For more information about R and ggplot2, please refer to R language manual, ggplot2 module manual.
This example (ndn-tree-with-l2tracer.cc) demonstrates basic usage of Packet-level trace helpers.
The corresponding topology file (topo-tree-25-node.txt):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | router
# node comment yPos xPos
Rtr1 NA 3 9
Rtr2 NA 9 9
Rtr3 NA 15 9
Rtr7 NA 9 15
Rtr4 NA 3 21
Rtr5 NA 9 21
Rtr6 NA 15 21
Src1 NA 1 3
Src2 NA 3 3
Src3 NA 5 3
Src4 NA 7 3
Src5 NA 9 3
Src6 NA 11 3
Src7 NA 13 3
Src8 NA 15 3
Src9 NA 17 3
Dst1 NA 1 27
Dst2 NA 3 27
Dst3 NA 5 27
Dst4 NA 7 27
Dst5 NA 9 27
Dst6 NA 11 27
Dst7 NA 13 27
Dst8 NA 15 27
Dst9 NA 17 27
link
# srcNode dstNode bandwidth metric delay queue
Src1 Rtr1 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src2 Rtr1 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src3 Rtr1 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src4 Rtr2 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src5 Rtr2 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src6 Rtr2 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src7 Rtr3 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src8 Rtr3 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Src9 Rtr3 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr1 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr2 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr3 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr4 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr5 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Rtr6 Rtr7 10Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst1 Rtr4 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst2 Rtr4 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst3 Rtr4 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst4 Rtr5 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst5 Rtr5 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst6 Rtr5 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst7 Rtr6 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst8 Rtr6 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
Dst9 Rtr6 100Mbps 1 10ms 10
|
Example simulation (ndn-tree-with-l2tracer.cc) scenario that utilizes trace helpers:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 | // ndn-simple-withl2tracer.cc
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/ndnSIM-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
AnnotatedTopologyReader topologyReader ("", 10);
topologyReader.SetFileName ("src/ndnSIM/examples/topologies/topo-tree-25-node.txt");
topologyReader.Read ();
/****************************************************************************/
// Install CCNx stack on all nodes
ndn::StackHelper ccnxHelper;
ccnxHelper.SetContentStore ("ns3::ndn::cs::Lru", "MaxSize", "1000");
ccnxHelper.SetForwardingStrategy ("ns3::ndn::fw::BestRoute");
ccnxHelper.InstallAll ();
/****************************************************************************/
// Installing global routing interface on all nodes
ndn::GlobalRoutingHelper ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper;
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.InstallAll ();
/****************************************************************************/
// Getting containers for the consumer/producer
Ptr<Node> consumer1 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src1");
Ptr<Node> consumer2 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src2");
Ptr<Node> consumer3 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src3");
Ptr<Node> consumer4 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src4");
Ptr<Node> consumer5 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src5");
Ptr<Node> consumer6 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src6");
Ptr<Node> consumer7 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src7");
Ptr<Node> consumer8 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src8");
Ptr<Node> consumer9 = Names::Find<Node> ("Src9");
Ptr<Node> producer1 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst1");
Ptr<Node> producer2 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst2");
Ptr<Node> producer3 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst3");
Ptr<Node> producer4 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst4");
Ptr<Node> producer5 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst5");
Ptr<Node> producer6 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst6");
Ptr<Node> producer7 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst7");
Ptr<Node> producer8 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst8");
Ptr<Node> producer9 = Names::Find<Node> ("Dst9");
/****************************************************************************/
ndn::AppHelper consumerHelper ("ns3::ndn::ConsumerCbr");
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Frequency", StringValue ("1000"));//interests per Second
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Randomize", StringValue ("uniform"));
/****************************************************************************/
// on the first to ninth consumer node install a Consumer application
// that will express interests in /dst1 to /dst9 namespace
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst9");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer1);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst8");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer2);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst7");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer3);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst6");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer4);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst5");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer5);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst4");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer6);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst3");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer7);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst2");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer8);
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst1");
consumerHelper.Install (consumer9);
/****************************************************************************/
ndn::AppHelper producerHelper ("ns3::ndn::Producer");
producerHelper.SetAttribute ("PayloadSize", StringValue("1024"));
/****************************************************************************/
// Register /dst1 to /dst9 prefix with global routing controller and
// install producer that will satisfy Interests in /dst1 to /dst9 namespace
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst1", producer1);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst1");
producerHelper.Install (producer1);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst2", producer2);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst2");
producerHelper.Install (producer2);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst3", producer3);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst3");
producerHelper.Install (producer3);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst4", producer4);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst4");
producerHelper.Install (producer4);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst5", producer5);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst5");
producerHelper.Install (producer5);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst6", producer6);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst6");
producerHelper.Install (producer6);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst7", producer7);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst7");
producerHelper.Install (producer7);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst8", producer8);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst8");
producerHelper.Install (producer8);
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/dst9", producer9);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/dst9");
producerHelper.Install (producer9);
/*****************************************************************************/
// Calculate and install FIBs
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.CalculateRoutes ();
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (10.0));
/****************************************************************************/
//Tracer:
L2RateTracer::InstallAll ("drop-trace.txt", Seconds (0.5));
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
|
To run this scenario, use the following command:
./waf --run=ndn-tree-with-l2tracer
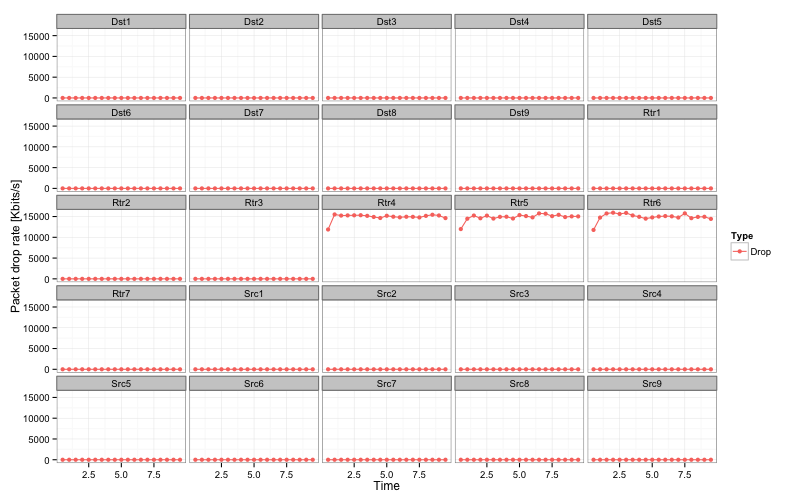
The successful run will create drop-trace.txt file in the current directly, which can be analyzed manually or used as input to some graph/stats packages.
For example, the following R script will build a number of nice graphs:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | #!/usr/bin/env Rscript
# Copyright (c) 2012-2013 Alexander Afanasyev <alexander.afanasyev@ucla.edu>
# install.packages ('ggplot2')
library (ggplot2)
## # install.packages ('scales')
## library (scales)
#########################
# Rate trace processing #
#########################
data = read.table ("drop-trace.txt", header=T)
data$Node = factor (data$Node)
data$Kilobits <- data$Kilobytes * 8
data$Type = factor (data$Type)
## data.rtr = data[grep("Rtr", data$Node),]
# graph rates on all nodes in Kilobits
g.all <- ggplot (data, aes (x=Time, y=Kilobits, color=Type)) +
geom_point (size=2) +
geom_line () +
ylab ("Packet drop rate [Kbits/s]") +
facet_wrap (~ Node) +
theme_bw ()
png ("drop-trace-all-nodes.png", width=800, height=500)
print (g.all)
x = dev.off ()
|
With the use of ndn::CsTracer it is possible to obtain statistics of cache hits/cache misses on simulation nodes.
The following code enables content store tracing:
// the following should be put just before calling Simulator::Run in the scenario ndn::CsTracer::InstallAll ("cs-trace.txt", Seconds (1)); Simulator::Run (); ...
This example (ndn-tree-cs-tracers.cc) demonstrates basic usage of content store tracer.
In this scenario we will use the same tree-like topology as in previous example, where consumers are installed on leaf nodes and producer is in the root of the tree. The main difference is that each client request data from the same namespace: /root/1, /root/2, ... Another small difference is that in this scenario we start our application not at the same time, but 10 ms apart.
Example simulation (ndn-tree-cs-tracers.cc) scenario that utilizes trace helpers:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | // ndn-tree-cs-tracers.cc
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/ndnSIM-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
AnnotatedTopologyReader topologyReader ("", 1);
topologyReader.SetFileName ("src/ndnSIM/examples/topologies/topo-tree.txt");
topologyReader.Read ();
// Install CCNx stack on all nodes
ndn::StackHelper ndnHelper;
ndnHelper.SetForwardingStrategy ("ns3::ndn::fw::BestRoute");
ndnHelper.SetContentStore ("ns3::ndn::cs::Lru", "MaxSize", "100"); // default ContentStore parameters
ndnHelper.InstallAll ();
// Installing global routing interface on all nodes
ndn::GlobalRoutingHelper ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper;
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.InstallAll ();
// Getting containers for the consumer/producer
Ptr<Node> consumers[4] = { Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-1"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-2"),
Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-3"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-4") };
Ptr<Node> producer = Names::Find<Node> ("root");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
ndn::AppHelper consumerHelper ("ns3::ndn::ConsumerCbr");
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Frequency", StringValue ("10")); // 100 interests a second
// Each consumer will express the same data /root/<seq-no>
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root");
ApplicationContainer app = consumerHelper.Install (consumers[i]);
app.Start (Seconds (0.01 * i));
}
ndn::AppHelper producerHelper ("ns3::ndn::Producer");
producerHelper.SetAttribute ("PayloadSize", StringValue("1024"));
// Register /root prefix with global routing controller and
// install producer that will satisfy Interests in /root namespace
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/root", producer);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root");
producerHelper.Install (producer);
// Calculate and install FIBs
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.CalculateRoutes ();
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (20.0));
ndn::CsTracer::InstallAll ("cs-trace.txt", Seconds (1));
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
|
To run this scenario, use the following command:
./waf --run=ndn-tree-cs-tracers
The successful run will create cs-trace.txt, which similarly to trace file from the tracing example can be analyzed manually or used as input to some graph/stats packages.
With the use of ndn::AppDelayTracer it is possible to obtain data about for delays between issuing Interest and receiving corresponding Data packet.
The following code enables application-level Interest-Data delay tracing:
// the following should be put just before calling Simulator::Run in the scenario ndn::AppDelayTracer::InstallAll ("app-delays-trace.txt"); Simulator::Run (); ...Output file format is tab-separated values, with first row specifying names of the columns. Refer to the following table for the description of the columns:
Column Description Time simulation time when SeqNo was receivied Node node id, global unique AppId app id, local unique on the node, not global SeqNo seq number of the Interest-Data Type Type of delay:
- LastDelay means that DelayS and DelayUS represent delay between last Interest sent and Data packet received
- FullDelay means that DelayS and DelayUS represent delay between first Interest sent and Data packet received (i.e., includes time of Interest retransmissions)
DelayS delay value, specified in seconds DelayUS delay value, specified in microseconds (10^-6) RetxCount number of Interest retransmissions (for LastDelay always equal to 1) HopCount combined number of number of hops for Interest and Data packet. Note that HopCount is increased anytime somebody calls Send method on a face, including delivery of Interest/Data to application via an AppFace (but not from application to ndn::L3Protocol!).
One consequence is that Interests satisfied by an app will have even hop count (min hop count = 2), and Interests satisfied from caches will have odd hop count (min hop count = 1)
This example (ndn-tree-app-delay-tracer.cc) demonstrates basic usage of application-level Interest-Data delay tracer.
In this scenario we will use the same tree-like topology as in packet trace helper example, where consumers are installed on leaf nodes and producer is in the root of the tree and clients request data from the same namespace: /root/1, /root/2, ...
Example simulation (ndn-tree-app-delay-tracer.cc) scenario that utilizes trace helpers:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | // ndn-tree-app-delay-tracer.cc
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/ndnSIM-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
AnnotatedTopologyReader topologyReader ("", 1);
topologyReader.SetFileName ("src/ndnSIM/examples/topologies/topo-tree.txt");
topologyReader.Read ();
// Install CCNx stack on all nodes
ndn::StackHelper ndnHelper;
ndnHelper.SetForwardingStrategy ("ns3::ndn::fw::BestRoute");
ndnHelper.InstallAll ();
// Installing global routing interface on all nodes
ndn::GlobalRoutingHelper ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper;
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.InstallAll ();
// Getting containers for the consumer/producer
Ptr<Node> consumers[4] = { Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-1"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-2"),
Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-3"), Names::Find<Node> ("leaf-4") };
Ptr<Node> producer = Names::Find<Node> ("root");
ndn::AppHelper consumerHelper ("ns3::ndn::ConsumerBatches");
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root");
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Batches", StringValue ("1s 1 10s 1"));
consumerHelper.Install (consumers[0]);
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Batches", StringValue ("11s 1"));
consumerHelper.Install (consumers[1]);
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Batches", StringValue ("11s 1"));
consumerHelper.Install (consumers[2]);
ndn::AppHelper producerHelper ("ns3::ndn::Producer");
producerHelper.SetAttribute ("PayloadSize", StringValue("1024"));
// Register /root prefix with global routing controller and
// install producer that will satisfy Interests in /root namespace
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.AddOrigins ("/root", producer);
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/root");
producerHelper.Install (producer)
.Start (Seconds (9));
// Calculate and install FIBs
ccnxGlobalRoutingHelper.CalculateRoutes ();
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (20.0));
ndn::AppDelayTracer::InstallAll ("app-delays-trace.txt");
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
|
To run this scenario, use the following command:
./waf --run=ndn-tree-app-delay-tracer
The successful run will create app-delays-trace.txt, which similarly to trace file from the packet trace helper example can be analyzed manually or used as input to some graph/stats packages.
This example (ndn-simple-with-pit-count-stats.cc) shows how you can periodically print out current size of PIT on the selected nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 | // ndn-simple-with-pit-count-stats.cc
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/point-to-point-module.h"
#include "ns3/ndnSIM-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
void
PeriodicStatsPrinter (Ptr<Node> node, Time next)
{
Ptr<ndn::Pit> pit = node->GetObject<ndn::Pit> ();
std::cout << Simulator::Now ().ToDouble (Time::S) << "\t"
<< node->GetId () << "\t"
<< Names::FindName (node) << "\t"
<< pit->GetSize () << "\n";
Simulator::Schedule (next, PeriodicStatsPrinter, node, next);
}
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
// setting default parameters for PointToPoint links and channels
Config::SetDefault ("ns3::PointToPointNetDevice::DataRate", StringValue ("1Mbps"));
Config::SetDefault ("ns3::PointToPointChannel::Delay", StringValue ("10ms"));
Config::SetDefault ("ns3::DropTailQueue::MaxPackets", StringValue ("20"));
// Read optional command-line parameters (e.g., enable visualizer with ./waf --run=<> --visualize
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
// Creating nodes
NodeContainer nodes;
nodes.Create (3);
// Connecting nodes using two links
PointToPointHelper p2p;
p2p.Install (nodes.Get (0), nodes.Get (1));
p2p.Install (nodes.Get (1), nodes.Get (2));
// see more http://www.nsnam.org/doxygen/classns3_1_1_names.html
Names::Add ("consumer", nodes.Get (0));
Names::Add ("router", nodes.Get (1));
Names::Add ("producer", nodes.Get (2));
// Install CCNx stack on all nodes
ndn::StackHelper ndnHelper;
ndnHelper.SetDefaultRoutes (true);
ndnHelper.SetPit ("ns3::ndn::pit::Persistent::AggregateStats");
ndnHelper.InstallAll ();
// set up periodic PIT stats printer on node 1
std::cout << "Time" << "\t"
<< "NodeId" << "\t"
<< "NodeName" << "\t"
<< "NumberOfPitEntries" << "\n";
Simulator::Schedule (Seconds (1), PeriodicStatsPrinter, nodes.Get (0), Seconds (1));
Simulator::Schedule (Seconds (1), PeriodicStatsPrinter, nodes.Get (1), Seconds (1));
Simulator::Schedule (Seconds (1), PeriodicStatsPrinter, nodes.Get (2), Seconds (1));
// Installing applications
// Consumer
ndn::AppHelper consumerHelper ("ns3::ndn::ConsumerCbr");
// Consumer will request /prefix/0, /prefix/1, ...
consumerHelper.SetPrefix ("/prefix");
consumerHelper.SetAttribute ("Frequency", StringValue ("10")); // 10 interests a second
consumerHelper.Install (nodes.Get (0)); // first node
// // Producer
ndn::AppHelper producerHelper ("ns3::ndn::Producer");
// Producer will reply to all requests starting with /prefix
producerHelper.SetPrefix ("/prefix");
producerHelper.SetAttribute ("PayloadSize", StringValue("1024"));
producerHelper.Install (nodes.Get (2)); // last node
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (20.0));
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
|
To run this scenario, use the following command:
./waf --run=ndn-simple-with-pit-count-stats